10 Stunning Azalea Bush Tips for a Thriving Garden Paradise
Welcome to the colorful world of azalea bushes! These stunning flowering shrubs are a favorite among gardeners for their vibrant blooms and relatively easy care. Whether you’re a seasoned green thumb or a beginner, this comprehensive guide will help you choose, plant, and nurture these beautiful plants. From the fiery hues of orange azalea bushes to the classic charm of red azalea bushes, we’ll explore everything you need to know to make your garden burst with color and life.
Understanding Azalea Bushes: Nature’s Paintbrush

What are Azalea Bushes?
Azaleas are flowering shrubs in the genus Rhododendron, known for their bright, showy flowers that bloom in spring. These versatile plants come in a wide range of sizes, colors, and varieties, making them suitable for various garden styles and climates. Azaleas are part of the Ericaceae family, which includes other popular garden plants like blueberries and heathers.
The History and Cultural Significance of Azaleas
Azaleas have a rich history dating back centuries. They were first cultivated in China and Japan, where they held great cultural significance. In Japan, azaleas are associated with the concept of wabi-sabi, which finds beauty in imperfection and transience. In the West, azaleas gained popularity in the 18th and 19th centuries, becoming a staple in many gardens, particularly in the southern United States.
Popular Azalea Varieties
Let’s explore some beloved azalea types:
- Encore Azaleas: Known for blooming multiple times a year, these azaleas offer extended color in the garden.
- Formosa Azaleas: Large, vigorous shrubs with pink to purple flowers, perfect for creating dramatic focal points.
- Flame Azaleas: Native to North America, featuring bright orange blooms that light up woodland gardens.
- Satsuki Azaleas: Compact Japanese varieties perfect for bonsai and small spaces.
- Kurume Azaleas: Known for their small leaves and profuse blooming, ideal for mass plantings.
- Exbury Azaleas: Deciduous azaleas with fragrant flowers in a range of warm colors.
- Gumpo Azaleas: Dwarf varieties that work well as ground covers or in rock gardens.
Azalea Bush Characteristics
Azaleas come in both deciduous and evergreen varieties. Deciduous azaleas lose their leaves in winter, while evergreen types maintain their foliage year-round. The flowers can be single, double, or semi-double, and come in a vast array of colors including white, pink, red, purple, and multicolor varieties.
Azalea Bush Care: Nurturing Your Colorful Companions

Planting Your Azalea Bush
Proper planting is crucial for healthy azaleas. Follow these steps:
- Choose a location with partial shade. Most azaleas prefer morning sun and afternoon shade.
- Ensure well-draining, acidic soil (pH 4.5-6.0). If your soil is alkaline, consider amending it with sulfur or peat moss.
- Dig a hole twice the width of the root ball and at the same depth.
- Gently remove the plant from its container and loosen the roots if they’re tightly bound.
- Place the plant in the hole, making sure the top of the root ball is level with or slightly above the soil surface.
- Backfill with soil, firming gently to remove air pockets.
- Water thoroughly and add a 2-3 inch layer of organic mulch, keeping it away from the stem.
Watering and Fertilizing
Azaleas prefer consistent moisture but can’t tolerate waterlogged soil. Water deeply once a week, more during dry spells or hot weather. To check soil moisture, stick your finger about 2 inches into the soil near the plant. If it feels dry, it’s time to water.
Fertilize with an acid-forming, slow-release fertilizer in early spring, just as new growth begins. Look for fertilizers specifically formulated for azaleas and rhododendrons. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive growth and reduced blooming.
Soil and pH Requirements
Azaleas thrive in acidic soil with a pH between 4.5 and 6.0. If your soil is too alkaline, you can lower the pH by:
- Adding organic matter like peat moss or pine needles
- Using sulfur or aluminum sulfate
- Applying an acidifying fertilizer regularly
It’s a good idea to test your soil pH annually and adjust as needed to keep your azaleas healthy and blooming profusely.
Light Requirements
While most azaleas prefer partial shade, some varieties can tolerate more sun. In general:
- Morning sun and afternoon shade is ideal for most azaleas
- In cooler climates, they can handle more sun
- In hot climates, they may need more protection from intense afternoon sun
Temperature and Humidity
Azaleas are generally hardy in USDA zones 6-8, but some varieties can tolerate colder or warmer climates. They prefer:
- Moderate temperatures: 60-70°F (15-21°C) during the day
- Protection from harsh winds
- High humidity: If you live in a dry climate, consider misting your azaleas regularly
Pruning Azalea Bushes: Timing is Everything
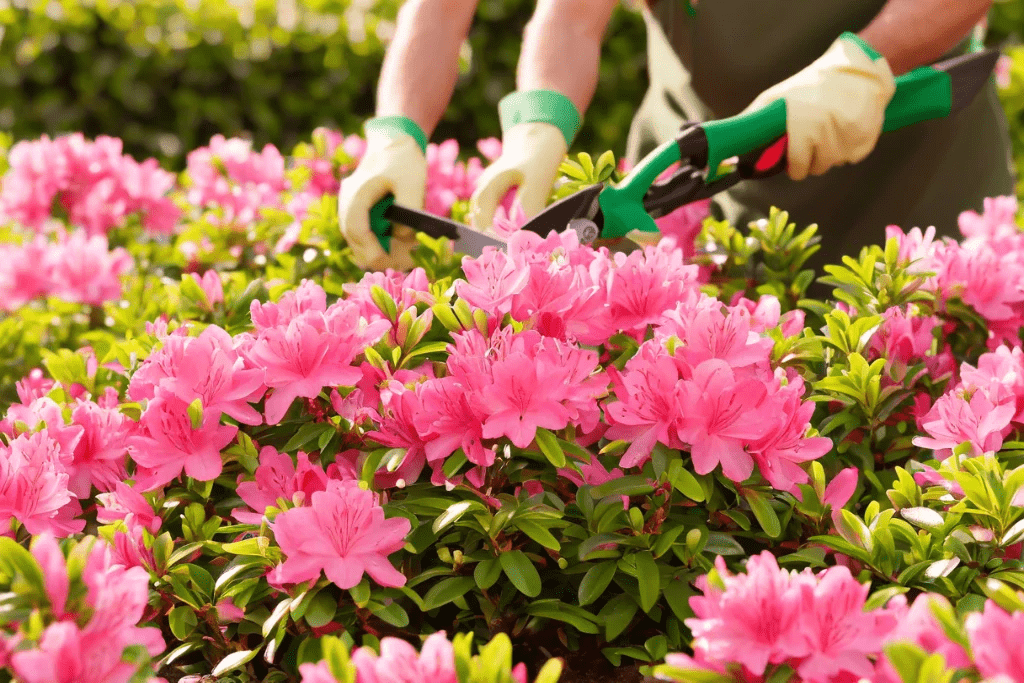

When to Trim Azalea Bushes
The best time to trim azalea bushes is right after they finish blooming in late spring or early summer. This allows the plant to develop new buds for the following year without sacrificing flowers. However, if you need to remove dead or diseased branches, this can be done at any time of the year.
How to Prune Azalea Bushes
Proper pruning helps maintain the shape and health of your azalea bushes. Here’s how to do it:
- Remove dead or diseased branches: Cut these off at their base or where they join a healthy branch.
- Thin out crowded areas for better air circulation: This helps prevent fungal diseases.
- Shape the bush by cutting back longer branches: Make cuts just above a leaf node or bud.
- Avoid cutting more than one-third of the plant in a single season to prevent stress.
- Use clean, sharp pruning shears to make clean cuts and prevent damage to the plant.
Rejuvenation Pruning
For older, overgrown azaleas, you might consider rejuvenation pruning:
- In late winter or early spring, cut the entire plant back to about 1 foot tall.
- As new growth appears, selectively prune to shape the plant.
- Be patient – it may take 2-3 years for the azalea to fully recover and bloom normally.
Read Also:
10 Amazing Swiss Cheese Plant Care Tips for Thriving Monstera Deliciosa
Troubleshooting Common Azalea Issues

Azalea Pests and Diseases
While azaleas are generally hardy, they can face some challenges. Watch out for:
- Lace bugs: These insects cause stippling on leaves. Control with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
- Spider mites: They create fine webbing and discoloration. Treat with a strong spray of water or miticide.
- Root rot: Caused by overwatering or poor drainage. Ensure proper soil drainage and avoid overwatering.
- Petal blight: A fungal disease that causes flowers to turn brown and mushy. Remove affected blooms promptly.
- Leaf gall: Causes swollen, distorted leaves. Remove affected leaves and improve air circulation.
Yellowing Leaves
If your azalea’s leaves are turning yellow, it could be due to:
- Iron deficiency: Common in alkaline soils. Treat with iron chelate or lower soil pH.
- Overwatering: Can lead to root problems. Ensure proper drainage and avoid waterlogged soil.
- Sunburn: Too much direct sunlight can cause leaf scorch. Provide more shade if necessary.
- Nitrogen deficiency: Apply a balanced, acid-forming fertilizer.
Winter Protection
In colder climates, azaleas may need winter protection:
- Apply a thick layer of mulch around the base of the plant
- Wrap the plant in burlap if extreme cold is expected
- Water thoroughly before the ground freezes to prevent winter desiccation
Propagating Azalea Bushes

Propagation by Cuttings
One of the easiest ways to propagate azaleas is through stem cuttings:
- Take 4-5 inch cuttings from soft, new growth in late spring or early summer.
- Remove lower leaves and dip the cut end in rooting hormone.
- Plant in a mix of peat moss and perlite.
- Keep the soil moist and place in a warm, bright location out of direct sunlight.
- Roots should develop in 4-8 weeks.
Layering
Another method of propagation is layering:
- Choose a low-growing, flexible branch.
- Make a small wound on the underside of the branch.
- Bend the branch to the ground and cover the wounded area with soil.
- Secure with a landscaping pin if necessary.
- Keep the soil moist. Roots should form in several months.
Read Also:
15 Essential Tips for Thriving Philodendron Selloum: A Complete Care Guide
Landscaping with Azalea Bushes: Design Ideas

Creating an Azalea Garden
Azaleas can be the star of your garden landscape. Here are some ideas:
- Use different varieties for a range of colors and bloom times
- Plant in groups for a dramatic effect
- Combine with other shade-loving plants like ferns, hostas, and camellias
- Create a woodland garden with azaleas as the understory planting
- Use azaleas to line a pathway or frame an entrance
Azaleas in Containers
Azaleas can thrive in containers, making them perfect for patios, balconies, or entryways:
- Choose compact varieties like Satsuki azaleas
- Use well-draining, acidic potting mix
- Ensure adequate drainage in the container
- Water more frequently, as containers dry out faster than in-ground plantings
- Bring containers indoors or provide extra protection in harsh winters
Companion Plants for Azaleas
Azaleas play well with many other plants. Consider pairing them with:
- Rhododendrons: Close cousins with similar care requirements
- Japanese Maples: Provide beautiful foliage contrast
- Bleeding Hearts: Add delicate texture and color
- Hellebores: Offer winter and early spring interest
- Coral Bells: Provide colorful foliage throughout the season
Choosing the Right Azalea for Your Space
Considering Size and Growth Rate
Azaleas come in a wide range of sizes to suit any garden:
- Dwarf varieties: 2-3 feet tall, perfect for small spaces or containers
- Medium-sized: 4-6 feet tall, ideal for foundation plantings or mixed borders
- Large varieties: Can reach 8-10 feet or more, great for privacy screens or woodland gardens
Growth rates vary, but most azaleas grow relatively slowly, adding 1-2 feet per year until they reach maturity.
Climate Considerations
Most azaleas thrive in USDA zones 6-8, but some varieties can tolerate colder or warmer climates. Always check the specific needs of your chosen variety. For example:
- Northern Lights series: Hardy to zone 4
- Encore Azaleas: Can tolerate the heat of zone 9
- Native azalea species: Often more adaptable to local conditions
Color Selection
Azaleas offer a rainbow of color options:
- White: Creates a clean, classic look
- Pink: Ranges from soft pastels to vibrant hot pink
- Red: Adds a bold pop of color
- Purple: Offers a regal touch to the garden
- Orange: Brings warmth and energy
- Multicolor: Some varieties feature flowers with multiple colors or color changes as the bloom ages
You Ma Also Like To Read:
Seasonal Care for Azalea Bushes

Spring Care
- Prune after blooming if needed
- Fertilize with a slow-release, acid-forming fertilizer
- Monitor for pests as new growth emerges
- Remove spent blooms (deadheading) to encourage bushier growth
Summer Care
- Water deeply during dry spells
- Apply mulch to retain moisture and suppress weeds
- Watch for signs of stress from heat or drought
Fall Care
- Reduce watering as temperatures cool
- Stop fertilizing to allow the plant to prepare for dormancy
- Plant new azaleas in early fall to allow root establishment before winter
Winter Care
- Protect from harsh winds and extreme cold
- Water occasionally during dry periods when the ground isn’t frozen
- Avoid heavy snow accumulation on branches
Frequently Asked Questions About Azalea Bushes
How big do azaleas get?
Azalea size varies greatly depending on the variety. They can range from compact 2-foot shrubs to large 10-foot bushes. Always check the mature size of your chosen variety when planning your garden layout.
Are azaleas deer resistant?
While no plant is entirely deer-proof, azaleas are not a favorite food for deer. However, in areas with high deer populations, protection may be necessary. Consider using deer repellents or physical barriers if deer are a problem in your area.
Can azaleas grow in full sun?
Most azaleas prefer partial shade, but some varieties can tolerate full sun with adequate moisture. In general, azaleas in cooler climates can handle more sun than those in hotter regions. Always check the specific needs of your chosen variety and observe your plant for signs of stress if planted in full sun.
How long do azaleas bloom?
The blooming period for azaleas typically lasts 2-3 weeks in spring. However, some varieties, like Encore Azaleas, can bloom multiple times throughout the growing season, extending the color show in your garden.
Are azaleas toxic to pets?
Yes, azaleas are toxic to dogs, cats, and horses if ingested. All parts of the plant contain grayanotoxins, which can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe cases, cardiovascular problems. If you have pets, consider planting azaleas in areas they can’t access or choose pet-safe alternatives.
How often should I fertilize my azaleas?
Generally, azaleas benefit from fertilization once a year in early spring. Use a slow-release, acid-forming fertilizer specifically formulated for azaleas and rhododendrons. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive growth and reduced blooming.
Can I change the color of my azalea flowers?
Unlike hydrangeas, the flower color of azaleas is genetically determined and cannot be changed by altering soil pH. To change the color in your garden, you’ll need to plant a different variety.
Conclusion: Embracing the Beauty of Azalea Bushes
From the vibrant orange azalea bush to the classic red azalea bush, these versatile shrubs offer endless possibilities for your garden. With their stunning blooms, relatively easy care requirements, and adaptability to various landscapes, azaleas have rightfully earned their place as a garden favorite.
By understanding their preferences for acidic soil, partial shade, and consistent moisture, you can create the perfect environment for these beautiful plants to thrive. Whether you’re creating a colorful hedge, a stunning focal point, or a container garden, azaleas are sure to bring joy and beauty to your outdoor space.
Remember, successful azalea care is all about balance – providing the right amount of sun, water, and nutrients while protecting them from extreme conditions. With proper care, including timely pruning and attention to their basic needs, azaleas will reward you with stunning blooms year after year.
So why not add some azalea magic to your garden? With their wide range of colors, sizes, and bloom times, there’s an azalea bush perfect for every gardener and every landscape. Whether you’re drawn to the fiery hues of an orange azalea bush or the timeless elegance of a white variety, these versatile shrubs are sure to bring a splash of color and a touch of charm to your outdoor space.
Happy planting, and may your garden flourish with the vibrant beauty of azaleas!
References
- American Rhododendron Society – This organization provides in-depth knowledge about azaleas, including planting guides, care, and troubleshooting issues like pests and diseases. They also offer resources on different azalea varieties.
- University of Georgia Extension – A comprehensive resource on growing azaleas in different climates, including details on soil requirements, pruning techniques, and common issues.
- Royal Horticultural Society (RHS) – The RHS offers an expert guide on azalea care, from planting tips to managing pests and diseases. They also provide detailed information on popular azalea varieties.
- Missouri Botanical Garden – A trusted source for information on azalea care, including propagation methods, soil recommendations, and climate considerations.



